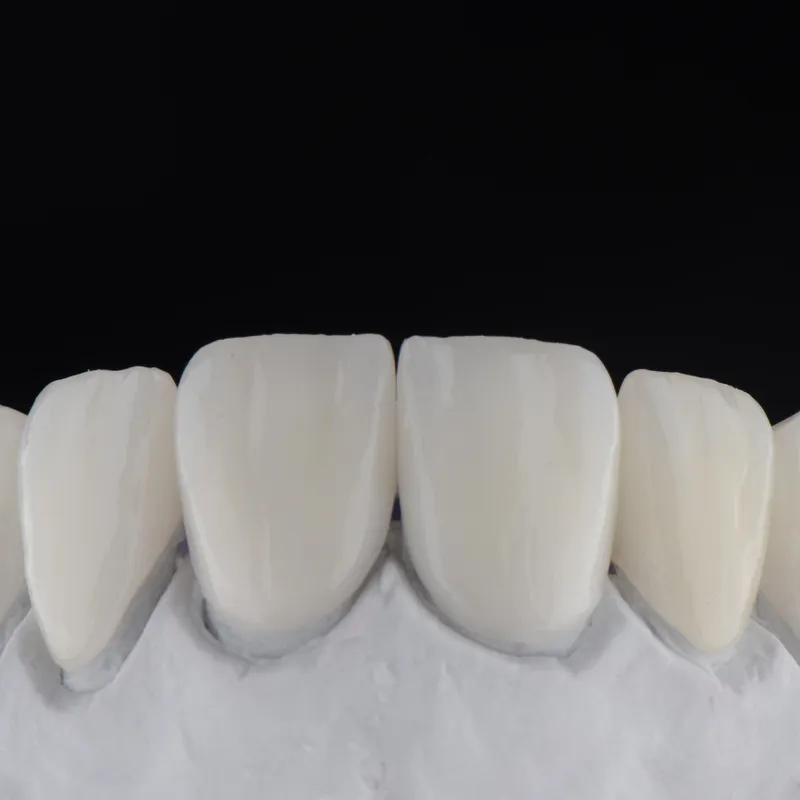
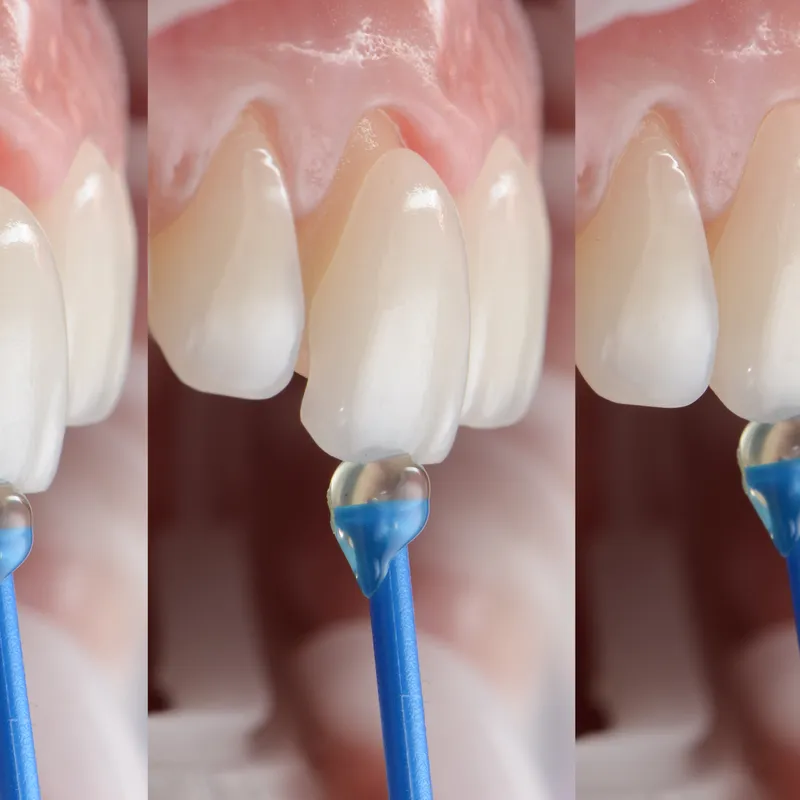
This kind of treatment is necessary in case of loosing one or several teeth. Also in the case of large-scale structural damage to tooth crowns. This field falls within restorative dentistry, focusing on rebuilding lost teeth and their structures using artificial materials. Dental prosthetics become necessary when one or more teeth are missing, or when significant structural damage occurs to dental crowns due to decay, erosion, or trauma. Final restorations primarily utilise various types of bioceramic materials, resembling natural teeth properties (e.g., glass ceramics, zirconia oxide ceramics, feldspathic ceramics, etc.). Temporary restorations and plate-type prostheses are crafted from various plastic materials.
Why is it necessary?
Timely and high-quality dental prosthetics help prevent certain undesirable changes within the mouth, such as tooth shifting, bite deformities, or jawbone resorption. Moreover, they ensure even distribution of chewing forces and functionality, restore dental arch integrity, enhance aesthetic appearance, and extend the lifespan of damaged teeth in the mouth.
How does the process of dental prosthetics unfold?
Let's break it down into key stages.
Consultation:
First, the patient undergoes a thorough examination. The dentist assists in selecting the most suitable treatment plan based on the individual situation.
Smile Design:
For extensive dental prosthetic work, particularly involving front teeth, a digital smile design is crafted. In the lab, a model of the anticipated restorations is meticulously prepared. This model can then be transferred to the patient's teeth using temporary materials for assessment.
Tooth Preparation for Prosthetics:
Damaged tooth surfaces are restored using filling materials, and any necessary reshaping is done by grinding. The space required for the prosthesis is digitally captured or taken with specialised impression materials. Temporary restorations are then prepared accordingly.
Measurement and Cementation of Restorations:
Final restorations, meticulously crafted in the laboratory, undergo measurement and evaluation for both aesthetic appeal and functionality. Once their fit is flawless, they are carefully cemented onto the prepared tooth surfaces.
Restoration Care:
It is crucial to maintain prosthetic teeth with care, including the use of toothbrushes, interdental brushes, and floss. Regular visits to the dentist and dental hygienist are necessary to preserve their functionality and appearance.
What are they?
Dental veneers are great solution to hide imperfections like color mismatches, uneven shapes, or awkward positioning. They're perfect for anyone craving a flawless smile, especially if you're not happy with the current look, size, or color of your teeth. Whether it's a single tooth or a whole row, veneers are carefully crafted to blend seamlessly with your natural teeth. You've got two options to choose from: the deluxe ceramic veneers, renowned for their top-notch aesthetics and durability, or the budget-friendly composite ones, which, while not as robust, still do the job well.
What's the procedure like?
It starts with a sit-down where we chat about your dream smile, taking into account your unique features and desires. Some photos will be taken and all the essential data will be gathered in order to create a digital preview of your future smile, which will be presented to you during your next visit. Then, our coleagues in the lab craft a blueprint for your new look. When it's time for your next visit, we'll be prepping your teeth for their makeover. We perform minor adjustments and refinements under the comfort of local anesthesia. Once your teeth are prepared, we take precise impressions and fit you with temporary veneers to maintain your smile while your custom ceramic veneers are being fabricated. After a few additional visits to ensure optimal fit and appearance, your final veneers are meticulously applied, ready to enhance your smile beautifully.
Taking care of Dental Veneers
To maintain a beautiful smile, it is essential to regularly visit your dentist and dental hygienist, as well as consistently and properly use toothbrushes and dental floss. You should take care of your dental veneers just like your natural teeth to ensure they last as long as possible.
One of the most common methods for restoring lost teeth is implant-supported prosthetics.
What's the procedure like?
After the specified healing period following implantation and once the implants have successfully integrated, the prosthetic process begins. The positions of the implants are recorded using digital methods or impression materials, and the chosen type of prosthesis is created. During additional visits, adjustments are made if necessary, and the prosthesis is secured onto the implants.
How to take care of implant-supported prosthetics?
Just like natural teeth, implant-supported prosthetics require proper at-home care and regular dental check-ups to maintain their function and prevent inflammation of the tissues around the implant. Brushing and flossing are still essential. After the prosthesis is placed on the implant, an individualized care plan for the teeth, gums, and implants is created for each patient.
In certain cases, it is not possible to place a dental implant in the location of a missing tooth. Instead, fixed bridges can be attached to the adjacent teeth.
Procedure Steps:
The patient undergoes a comprehensive examination, during which the dentist assists in selecting the most appropriate treatment option and formulates a treatment plan. The area where the prosthesis will be placed is captured either digitally or using special impression materials. The final restorations are then prepared in a laboratory, meticulously measured, and evaluated for their aesthetic appearance and functionality. Once the fit is flawless, they are securely attached to the teeth adjacent to the missing tooth site.
Restoration Care:
It is crucial to maintain prosthetic teeth with care, including the use of toothbrushes, interdental brushes, and floss. Regular visits to the dentist and dental hygienist are necessary to preserve their functionality and appearance.
To restore the structure of damaged teeth, the latest biomimetic principles are applied, helping to preserve the remaining healthy tissues and vitality, while restoring the natural function and biomechanics of the tooth. Depending on the extent of tooth structure loss, specific restorations such as onlays, inlays, veneers, or crowns are used.
These restorations vary in coverage: inlays and onlays are used to repair moderate to large structural defects in the crowns of molars and premolars. Crowns, which cover the entire surface of the tooth, are used in cases where the posterior and anterior teeth cannot be restored with simpler methods.
For the prosthetic restoration of edentulous jaws, the following options are available:
Removable dentures, which only restore a portion of the chewing force, making it difficult to chew harder foods. During chewing, the denture can press against and traumatise the oral mucosa, causing it to move. While many people manage to adapt to the limitations of removable dentures, some never do.
Implant-supported dentures are more comfortable and restore a significant portion of the chewing force. There are several options for this type of prosthesis: implant-supported dentures, segmental bridge prostheses, or horseshoe-shaped bridge prostheses.
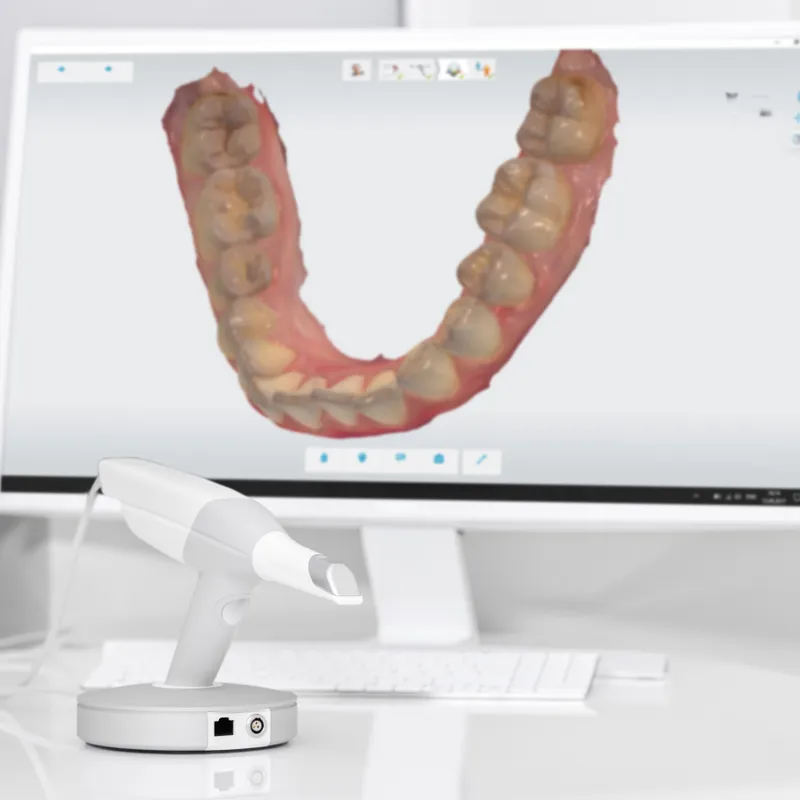
In extensive dental prosthetics, particularly for anterior teeth, a specialized 3D intraoral scanner is employed to scan the patient's mouth, capturing high-quality images of the smile.
These images are then transferred to a dedicated computer program, where a digital smile design is crafted in collaboration with the patient. This approach allows for a preview of the final outcome before treatment commences. Subsequently, in the laboratory, a model of the planned restorations is meticulously crafted. This model, made from temporary materials, is then transferred to the patient's teeth, enabling an evaluation of the anticipated result.
Hybrid ceramic restoration of a lateral tooth: €450
Zirconia oxide/glass ceramic restoration of a lateral tooth: €500
Zirconia oxide/glass ceramic restoration of a front tooth: €600
Feldspathic veneer: €750
Individual restoration of a front tooth with zirconia oxide/glass ceramic (complex case): €800
Zirconia oxide restoration of a lateral area implant: €670
Zirconia oxide and glass ceramic hybrid restoration of a lateral area implant: €750
Zirconia oxide restoration of a front area implant: €770
Zirconia oxide and glass ceramic hybrid restoration of a front area implant: €850
Individual restoration of a front area implant with zirconia oxide and glass ceramic hybrid (complex case): €900